Trong bài toán học máy, khi dữ liệu bị mất cân bằng (imbalanced data), mô hình có xu hướng thiên lệch về phía lớp chiếm đa số. Một cách phổ biến để giải quyết vấn đề này là sử dụng hàm mất mát (loss function) tùy chỉnh, nhằm phạt nặng hơn những lỗi thuộc lớp thiểu số.
Dưới đây là một số cách phổ biến để xây dựng hàm mất mát tùy chỉnh cho dữ liệu mất cân bằng:
✅ 1. Weighted Cross-Entropy Loss
Gán trọng số lớn hơn cho lớp thiểu số.
Ví dụ với PyTorch:
import torch import torch.nn as nn # Giả sử có 2 lớp: lớp 0 chiếm 90%, lớp 1 chiếm 10% class_weights = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.9]) # Trọng số nghịch đảo tỷ lệ criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=class_weights)
✅ Lưu ý: Cần tính tỷ lệ xuất hiện của từng lớp từ dữ liệu huấn luyện để chọn trọng số hợp lý.
✅ 2. Focal Loss
Được thiết kế để tập trung hơn vào các ví dụ khó học (thường là lớp thiểu số).
Công thức:
Trong các bài toán phân loại thường gặp, CrossEntropy Loss sẽ đối xử các mẫu như nhau. Nhưng khi có quá nhiều mẫu dễ (ví dụ lớp chiếm đa số), mô hình có xu hướng học tốt lớp đó và bỏ qua lớp thiểu số. Focal Loss xử lý điều này bằng cách:
- Giảm ảnh hưởng của các mẫu dễ phân loại.
- Tăng mức độ “tập trung” vào các mẫu khó hoặc lớp hiếm.
Công thức của Focal Loss dựa trên CrossEntropy Loss:
![]()
Trong đó:
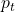 : độ tin cậy của mô hình cho lớp đúng (được tính từ output của softmax)
: độ tin cậy của mô hình cho lớp đúng (được tính từ output của softmax)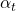 : trọng số của lớp (để xử lý mất cân bằng)
: trọng số của lớp (để xử lý mất cân bằng)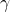 : tham số điều chỉnh (gamma càng lớn → mô hình càng tập trung vào các mẫu khó)
: tham số điều chỉnh (gamma càng lớn → mô hình càng tập trung vào các mẫu khó)
Ví dụ cài đặt PyTorch:
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, alpha=1, gamma=2, reduction='mean'):
super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
self.alpha = alpha
self.gamma = gamma
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
BCE_loss = nn.functional.cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduction='none')
pt = torch.exp(-BCE_loss)
focal_loss = self.alpha * (1 - pt) ** self.gamma * BCE_loss
if self.reduction == 'mean':
return focal_loss.mean()
elif self.reduction == 'sum':
return focal_loss.sum()
else:
return focal_loss
✅ 3. Label Smoothing + Weighting
Kết hợp label smoothing (giảm overconfidence) với trọng số lớp.
✅ 4. Custom Class-Balanced Loss
Theo công thức trong bài báo “Class-Balanced Loss Based on Effective Number of Samples” (CVPR 2019)
Công thức trọng số:
![]()
với![]() =số mẫu trong lớp c
=số mẫu trong lớp c ![]() giá trị gần 1 (ví dụ 0.999)
giá trị gần 1 (ví dụ 0.999)
✅ Gợi ý lựa chọn:
| Tình huống | Hàm mất mát đề xuất |
|---|---|
| Mất cân bằng nhẹ | Weighted CrossEntropy |
| Mất cân bằng nặng | Focal Loss hoặc Class-Balanced Loss |
| Dữ liệu nhiễu | Focal Loss với label smoothing |
📦 Nhập thư viện cần thiết
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import classification_report import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader
Sử dụng pandas, numpy, scikit-learn cho tiền xử lý và đánh giá mô hình. torch cung cấp các công cụ cần thiết để xây dựng và huấn luyện mạng nơ-ron với PyTorch.
📁 Tải và xử lý dữ liệu Parkinson
data = pd.read_csv('http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/parkinsons/parkinsons.data')
data = data.drop(['name'], axis=1)
X = data.drop(['status'], axis=1).values
y = data['status'].values
Tải dữ liệu từ UCI ML Repository, loại bỏ cột ‘name’ (không dùng cho huấn luyện), tách đặc trưng (X) và nhãn (y), với status là 0 (bình thường) hoặc 1 (bệnh Parkinson).
🧪 Chia dữ liệu thành tập huấn luyện và kiểm tra
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, stratify=y, random_state=42)
Chia dữ liệu thành 80% huấn luyện và 20% kiểm tra. Dùng stratify để đảm bảo tỷ lệ lớp được giữ nguyên.
🔄 Chuyển dữ liệu thành Tensor để dùng trong PyTorch
X_train_tensor = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32) y_train_tensor = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.long) X_test_tensor = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32) y_test_tensor = torch.tensor(y_test, dtype=torch.long)
Chuyển dữ liệu từ NumPy array sang PyTorch tensors để tương thích với mô hình.
🧺 Tạo DataLoader để hỗ trợ việc huấn luyện theo mini-batch
train_dataset = TensorDataset(X_train_tensor, y_train_tensor) train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True)
Gói dữ liệu huấn luyện thành DataLoader để lặp qua các mini-batch và shuffle nhằm tăng chất lượng huấn luyện.
🧠 Định nghĩa mô hình mạng nơ-ron đơn giản
class SimpleNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(X.shape[1], 64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(64, 2)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
Mạng gồm 1 lớp ẩn với 64 neurons và hàm ReLU, đầu ra là softmax gồm 2 lớp (tương ứng bệnh và không bệnh).
🔥 Xây dựng Focal Loss để xử lý mất cân bằng lớp
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, alpha=[1.0, 3.0], gamma=2):
super().__init__()
self.alpha = torch.tensor(alpha, dtype=torch.float32)
self.gamma = gamma
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
ce_loss = F.cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduction='none')
pt = torch.exp(-ce_loss)
at = self.alpha[targets]
focal_loss = at * (1 - pt) ** self.gamma * ce_loss
return focal_loss.mean()
Focal Loss giảm trọng số của các mẫu dễ phân loại và tăng cho các mẫu khó, hỗ trợ lớp hiếm. alpha điều chỉnh trọng số từng lớp, gamma kiểm soát độ nhấn mạnh.
🏋️ Hàm huấn luyện và đánh giá mô hình
def train_and_evaluate(loss_fn, description):
model = SimpleNN()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
for epoch in range(20):
model.train()
for xb, yb in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(xb)
loss = loss_fn(output, yb)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluation
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(X_test_tensor)
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1).numpy()
print(f"\n=== {description} ===")
print(classification_report(y_test, preds))
Huấn luyện mô hình trong 20 epochs, tính loss và cập nhật trọng số. Sau huấn luyện, dùng tập kiểm tra để đánh giá hiệu suất bằng classification_report.
📊 Chạy thử với các phương pháp loss khác nhau
CrossEntropy bình thường:
train_and_evaluate(nn.CrossEntropyLoss(), "CrossEntropy (No Weight)")
Không xử lý mất cân bằng lớp.
CrossEntropy có trọng số theo tần suất lớp:
num_0, num_1 = sum(y_train == 0), sum(y_train == 1) weights = torch.tensor([1.0 / num_0, 1.0 / num_1], dtype=torch.float32) train_and_evaluate(nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=weights), "Weighted CrossEntropy")
Tính trọng số ngược với số lượng của từng lớp.
Focal Loss:
train_and_evaluate(FocalLoss(alpha=[3.0, 1.0]), "Focal Loss")
Ưu tiên lớp hiếm (đặt alpha lớn hơn).
Toàn bộ code
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader
# Load and prepare data
data = pd.read_csv('http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/parkinsons/parkinsons.data')
data = data.drop(['name'], axis=1)
X = data.drop(['status'], axis=1).values
y = data['status'].values
# Train-test split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, stratify=y, random_state=42)
# Convert to tensors
X_train_tensor = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train_tensor = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.long)
X_test_tensor = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32)
y_test_tensor = torch.tensor(y_test, dtype=torch.long)
train_dataset = TensorDataset(X_train_tensor, y_train_tensor)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True)
# Model
class SimpleNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(X.shape[1], 64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(64, 2)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
# Focal Loss
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, alpha=[1.0, 3.0], gamma=2):
super().__init__()
self.alpha = torch.tensor(alpha, dtype=torch.float32)
self.gamma = gamma
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
ce_loss = F.cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduction='none')
pt = torch.exp(-ce_loss)
at = self.alpha[targets]
focal_loss = at * (1 - pt) ** self.gamma * ce_loss
return focal_loss.mean()
# Training and evaluation
def train_and_evaluate(loss_fn, description):
model = SimpleNN()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
for epoch in range(20):
model.train()
for xb, yb in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(xb)
loss = loss_fn(output, yb)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluation
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(X_test_tensor)
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1).numpy()
print(f"\n=== {description} ===")
print(classification_report(y_test, preds))
# No weighting
train_and_evaluate(nn.CrossEntropyLoss(), "CrossEntropy (No Weight)")
# Weighted CrossEntropy
num_0, num_1 = sum(y_train == 0), sum(y_train == 1)
weights = torch.tensor([1.0 / num_0, 1.0 / num_1], dtype=torch.float32)
train_and_evaluate(nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=weights), "Weighted CrossEntropy")
# Focal Loss
train_and_evaluate(FocalLoss(alpha=[3.0, 1.0]), "Focal Loss")
Output:
=== CrossEntropy (No Weight) ===
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.38 0.50 0.43 10
1 0.81 0.72 0.76 29
accuracy 0.67 39
macro avg 0.60 0.61 0.60 39
weighted avg 0.70 0.67 0.68 39
=== Weighted CrossEntropy ===
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.67 0.40 0.50 10
1 0.82 0.93 0.87 29
accuracy 0.79 39
macro avg 0.74 0.67 0.69 39
weighted avg 0.78 0.79 0.78 39
=== Focal Loss ===
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.42 0.80 0.55 10
1 0.90 0.62 0.73 29
accuracy 0.67 39
macro avg 0.66 0.71 0.64 39
weighted avg 0.78 0.67 0.69 39
⚖️ CrossEntropy Loss (No Weight)
- Lớp 0 (bình thường):
- Precision = 0.38 → Khá thấp, nhiều dự đoán sai về lớp này.
- Recall = 0.50 → Chỉ nhận diện được một nửa số mẫu thực sự thuộc lớp 0.
- F1-score = 0.43 → Hiệu suất kém.
- Lớp 1 (Parkinson):
- Precision = 0.81 → Đa phần dự đoán lớp 1 là đúng.
- Recall = 0.72 → Nhận diện lớp 1 tốt hơn lớp 0.
➡️ Mô hình thiên vị lớp 1 vì đây là lớp chiếm đa số. Mặc định loss không xử lý mất cân bằng lớp nên lớp 0 bị “ngó lơ”.
⚖️ Weighted CrossEntropy
- Lớp 0:
- Precision = 0.67 → Khả năng phân biệt được cải thiện đáng kể.
- Recall = 0.40 → Tuy chưa cao nhưng giảm nhầm lẫn.
- Lớp 1:
- Precision = 0.82, Recall = 0.93 → Hiệu suất rất mạnh với lớp chính.
➡️ Accuracy tăng lên 79% và F1 macro cũng cao hơn. Việc thêm trọng số theo tần suất lớp giúp mô hình chú ý hơn đến lớp thiểu số, dù vẫn còn bỏ sót một số mẫu lớp 0.
🔥 Focal Loss
- Lớp 0:
- Precision = 0.42 → Vẫn khá thấp nhưng…
- Recall = 0.80 → Rất tốt, tức mô hình nhận diện được hầu hết các mẫu thuộc lớp 0.
- Lớp 1:
- Precision = 0.90 → Dự đoán chính xác lớp 1.
- Recall = 0.62 → Có xu hướng bỏ sót một số mẫu lớp 1.
➡️ Focal Loss tập trung mạnh vào các mẫu khó phân loại, dẫn đến việc ưu tiên lớp 0 (lớp thiểu số). Tuy accuracy không tăng, nhưng khả năng phát hiện lớp 0 đã cải thiện rõ rệt.
🧠 Tổng kết
| Loss Function | Accuracy | Lớp 0 Recall | Lớp 1 Recall | Chú thích |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrossEntropy (No Weight) | 67% | 50% | 72% | Thiên vị lớp đa số |
| Weighted CrossEntropy | 79% | 40% | 93% | Cân bằng tốt hơn, ưu lớp 1 |
| Focal Loss | 67% | 80% | 62% | Tăng cường lớp hiếm nhưng giảm lớp chính |
Nếu mục tiêu của bạn là phát hiện chính xác các ca bệnh Parkinson, thì Weighted CrossEntropy là lựa chọn tốt. Còn nếu bạn muốn giảm thiểu bỏ sót lớp bình thường, Focal Loss lại là phương án đáng cân nhắc.
Discover more from Cùng Học Cùng Mơ
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.